First, an e-commerce SEO audit and a general website SEO audit are not the same, as e- commerce sites tend to have dynamic content. Additionally, e-commerce websites often have 80% similar content due to the fixed nature of product specifications, which cannot be changed.
Hi, I am Tarun Pal, and I have been working as Digital Marketing Executive at Waffle Bytes for 2 years. I have done SEO audits for e-commerce sites many times for different clients.
I have completed the latest E-commerce SEO audit for my client named Robotools. Fortunately, after fixing technical, on-page, and off-page issues, this site’s products rank higher on search engines, even without having a high domain authority.
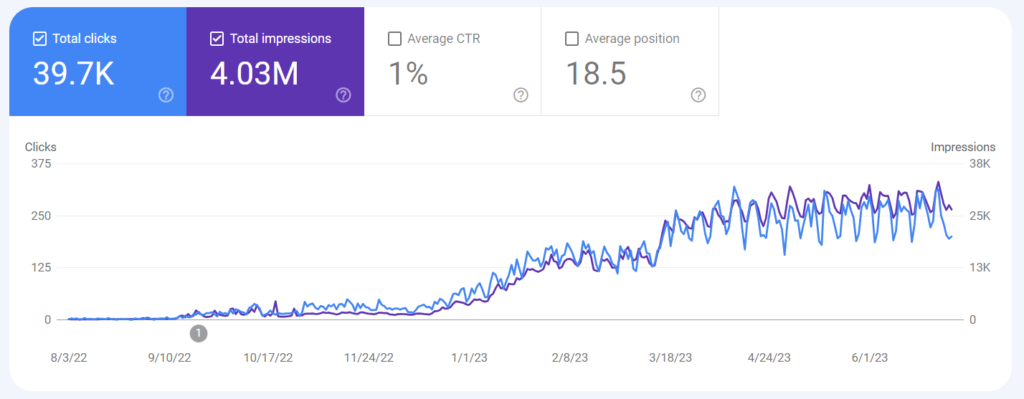
In this article, I will share with you a guide on how to conduct e-Commerce SEO successfully. If you are looking for a quick checklist, you can download it here: Ecommerce SEO Checklist – Google Sheets.
Well, I’m not starting with an explanation or definition, such as: what is e-Commerce SEO? Why it’s important or what it includes. Because I know you are a small business owner or SEO executive who is doing this for your boss or client, and I don’t need to explain to you what an e-Commerce SEO audit is and why it’s important. I know one thing you need: organic search traffic. So read till the end because it will give you something to remember on your SEO journey.
Let’s begin without wasting time!
Ecommerce – Technical SEO Audit
The first step for an SEO audit for an e-commerce website is to check for technical issues on the website. This is crucial because crawling and indexing depend on the website’s technical aspects, such as how well the e-commerce site performs when crawlers like Google bot visit it.
1. E-Commerce Site Structure
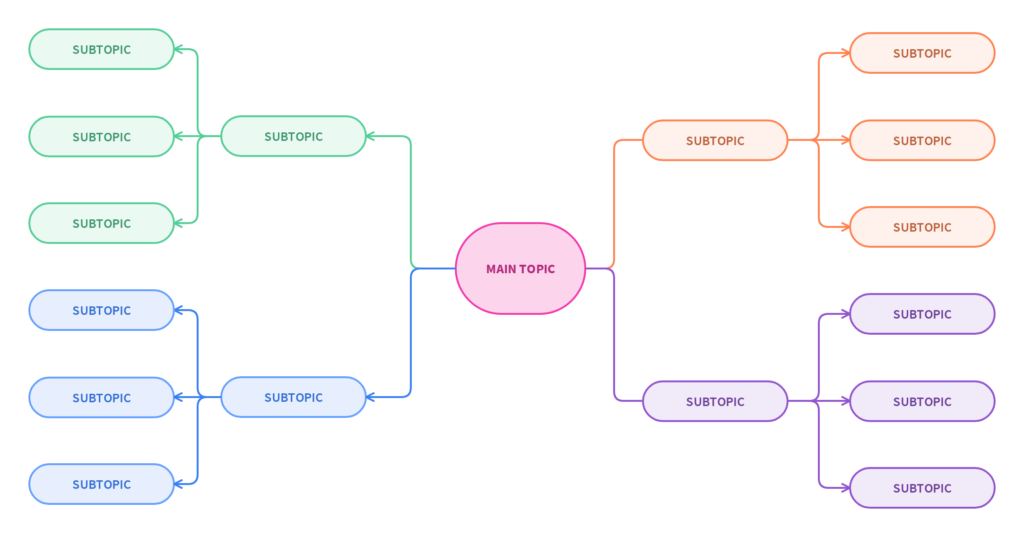
The structure of the website plays a crucial role not only for search engines but also for users. So while checking the site structure of an e-commerce website look navigation:
As you know, an e-commerce navigation contains pages like home, about us, sale, product categories, and sometimes nests genders in subdirectories. So the best practice is to link categories, then sub-categories, and finally products, because Google crawlers work on linkages. If it’s not possible to link all products to category pages, create a sitemap or use Google Merchandise Feed so Google can easily understand which products to index.
You can use brain mapping to define the site navigation structure. Here is an example of brain mapping:
2. Rotobs.txt
The robots.txt file is a small but impactful file for your site rankings. Test the robots.txt file with Google Search Console to determine which pages are allowed to be crawled and set the crawl budget. It is particularly helpful when you don’t want to index pages such as the admin panel, payment pages, or customer profile pages.
This is the simplest version of defining a robots.txt file for an e-commerce site, but if you want to block some pages or products, you can add them here:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /checkout/
Disallow: /cart/
Disallow: /account/
Disallow: /login/
Disallow: /register/
Disallow: /search/
Disallow: /wishlist/
Disallow: /compare/
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /checkout/*
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
If you want to read about robots.txt in full depth, you can find an excellent guide on Ahrefs. This is the best guide I have ever read: Robots.txt and SEO.
3. URL Structure
URLs are the addresses of your products for Google, yet many SEOs do not understand the importance of URL structure.

For example, you have a clothing e-commerce store and a collection of t-shirts with different colors, such as blue, black, and yellow. These are all product variants. But the question is, what is the URL structure for these products and their variants? Google recommends only two types of URLs for product variants: path segment structure like product/t-shirts/green and query parameters like /t-shirt?color=green. One more thing for canonicalization is that you have to add a canonical tag without query parameters or path segments.
So, check your e-commerce URLs now. If you find any problems, search for a solution on Google, or contact us for support. We are happy to help you regarding e-commerce URL structure.
4. XML Sitemap
An XML Sitemap is like a directory of pages, category pages, sub-category pages, and the products of your e-commerce store. There is nothing technical to do with sitemaps, but while conducting a technical audit, keep these things in mind:
- It should contain only the main canonical versions of your URLs, and ensure that these URLs are “clean” and do not contain any URL parameters.
- It should only list URLs that you actually want indexed, making sure that these URLs do not have “noindex” meta tags and are not blocked by robots.txt.
- It should be set to be automatically updated as pages are added or deleted from your site.
5. Meta Tags
While conducting an SEO audit for an e-commerce website, checking meta tags will be the 5th thing. There are some important meta tags that an e-commerce store should have.
| Meta Tag | Description |
<title> | Specifies the title of the webpage and appears in the browser’s title bar and search engine results. |
<meta name="description"> | Provides a brief summary of the webpage’s content, displayed in search engine results. |
<meta name="robots"> | Informs search engine crawlers whether to index the page and follow its links. |
<meta name="viewport"> | Defines how the page should be displayed on different devices and screen sizes (for responsive design). |
<meta name="author"> | Identifies the author of the webpage’s content. |
<meta name="canonical"> | Specifies the preferred URL for a duplicate or similar page (to avoid duplicate content issues). |
<meta name="referrer"> | Controls the amount of referrer information passed when a user clicks on a link from your page. |
So, let’s look at the necessary meta tags that an e-commerce website should contain for more information. You can check the meta tags guidelines that Google supports.
6. Canonical URLs
The e-commerce website has products and their variants, such as size, color, and many more.
- Region variants: For example, a piece of content for India and Australia, accessible from different URLs, but essentially the same content in the same language.
- Device variants: For example, a page with both a mobile and a desktop version.
- Protocol variants: For example, the HTTP and HTTPS versions of a site.
- Site functions: For example, the results of sorting and filtering functions on a category page.
- Accidental variants: For example, the demo version of the site is accidentally left accessible to crawlers.
These variants have a high chance of creating duplicate pages in your e-commerce store, and Google may have difficulty determining which page is the main page. Therefore, for better canonicalization, it’s important to use the ‘rel=canonical‘ tag on your website and pages.
7. Pagination
Pagination is part of the page experience, and page experience is a ranking signal on Google. So, for this, Google recommends three types of pagination methods:
Pagination is part of the page experience, and page experience is a ranking signal on Google. So, for this, Google recommends three types of pagination methods:
- Pagination: Users can use links such as “next,” “previous,” and page numbers to navigate between pages that display one page of results at a time.
- Load more: Buttons that users can click to extend an initial set of displayed results.
- Infinite scroll: Users can scroll to the end of the page to load more content.
Hence, check what kind of pagination method an e-commerce website has when you conduct an SEO audit. If the pagination does not have a series like example.com/page-1, load more button, or breaks between Infinite scroll, then it’s an issue
8. HTTP Status Codes
There are four categories of HTTPS status codes: 2xx (success), 3xx (redirection), 4xx (client errors), and 5xx (server errors). But we only need to check these while doing an SEO audit because you can access all of them without a web developer:
- 404 – Use tools like GSC and Ahrefs to find 404 pages on your website.
- Broken Links: Broken links are similar to 404 errors, but they involve links between pages. Check this and fix it.
- Redirects: There are two kinds of redirects: permanent redirects (301) and temporary redirects (302). Check all of them and refer to the GSC (Google Search Console) pages report.
9. Mobile Responsiveness
83% percent of consumers use their smartphones or mobile devices to make online purchases. This highlights the importance of mobile responsiveness as a sales aspect. Additionally, Google considers mobile responsiveness as a ranking factor. Hence, check your e-commerce website’s mobile responsiveness using the Mobile-Friendly Test or do it manually.
10. SSL Certificate
Ensure the website has an SSL certification because it is recommended for security reasons to have an SSL certification. For an e-commerce store, it is advised to have an Extended Validation (EV) Certificate. So, checking the website’s trustworthiness is the 11th thing while doing an SEO audit.
11. Schema Markup
Product structured data is a very important aspect for ranking your products higher in search engines because Google easily understands product schema with JSON format, enabling it to display product availability, price, and reviews on the search result page.
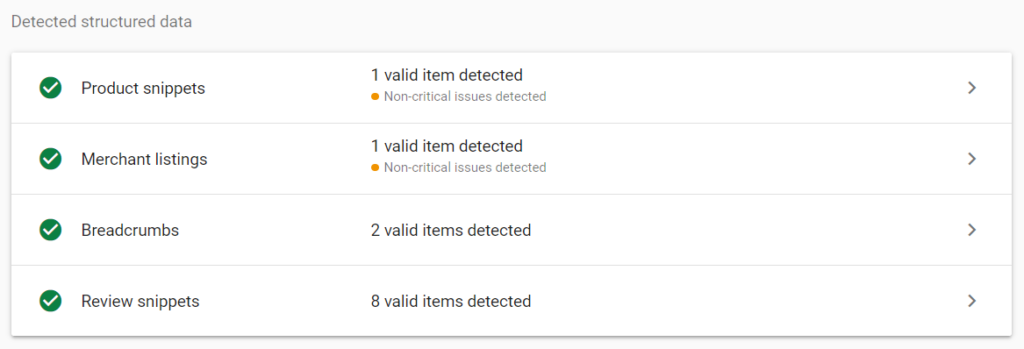
To check product structure data, use these two tools: schema markup validator and rich results test. If your product pages already have this, then that’s a good thing. If they don’t, you can prioritize this task while doing technical SEO.
E-Commerce – On-Page SEO Audit
An on-page SEO audit for an e-commerce website includes activities related to the content of the product pages and the page experience for users. This is the most important part of SEO, as even 50% of your ranking depends on on-page SEO activities.
12. Keyword Usage and Targeting
Check the keyword usage and targeting in all product pages and other pages as well. I will not advise you to stuff keywords in your product pages. Instead, think about what kind of details the page should contain when a user visits your product pages, such as color variants, size variants, specifications, price, customer reviews, availability, and FAQs about the product.
To analyze your target keywords, look at the keywords for which your competitors are ranking. You can use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush for a comprehensive keyword overview. This will help you understand the competitive landscape and identify valuable keywords to target for your SEO strategy.
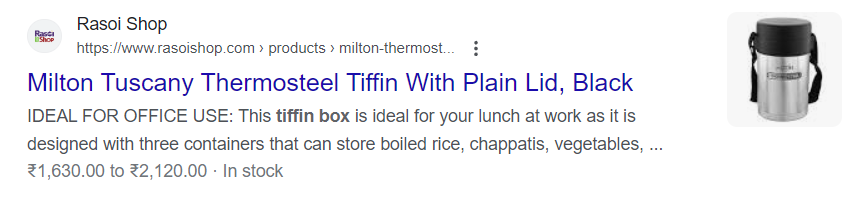
13. Product – Title & Meta Descriptions
The title is the first thing that your target audience will see in the Google search result page, and it also influences the Click-Through Rate (CTR). So, check and include all your keywords and Unique Selling Proposition (USP) such as free shipping or any ongoing offers on that product. Here is example of good title:
Description is the content that explains your pages to Google algorithms in a concise way. It provides a brief 160-character description of the product. This is the next thing to check in the e-Commerce SEO audit.
14. Heading Optimization (H1, H2, H3)
Make sure the product name is written in the H1 heading, and other elements should be prioritized with H2 and other heading tags. It is called semantic HTML, and there is a reason for using these tags. You can’t use H4 for the product title or change the size using CSS. So, check the page heading hierarchy manually by inspecting it using dev tools.
Here is short guide for heading tags:
- H1 – This heading is for mainly product main content, for example if your product name.
- H2 – The heading two is for specification, reviews and features.
- H3 – The third one is for the name of the users who is writing review on your site.
15. Internal Linking
The internal linking matters to SEO, as the search advocate at Google has stated that internal linking is ‘supercritical for SEO.’ He has also mentioned that internal linking presents an opportunity to communicate something more to Google than what internal navigational links can convey.
So, check how many internal links you currently have, and if your e-commerce website has 100 products, then the internal links should be more than 1000, dynamically utilizing anchor text.
16. Image Optimization
Image optimization is an essential aspect to check because many customers nowadays use Google Lens to search for products. Google utilizes machine learning and alt text to provide a good experience to the searchers.
There are three things to check in an e-commerce SEO audit:
- Image Format: Examine the image format your website is using. If it relies on formats like JPEG or PNG, these formats may not be ideal for page load speed. Instead, consider using WebP, a modern image format that offers superior lossless and lossy compression for web images.
- Image Alt Text: Check the image alt text. If the alt text consists of generic names like ‘image1’ or ‘image2,’ it may not be beneficial for product ranking in Google image results. Ensure that all images on your E-commerce website have descriptive names.
- Image Sizing: Determine if all product images have the same size or if they differ. If they are consistent in size, there shouldn’t be a problem. However, if the image sizes vary, it can become a complex issue when applying for Google Merchandise Store.
17. Social Media Integration
Social media integration is a crucial factor for social ranking signals because nowadays, every user looks for social media pages of brands and websites they visit. Therefore, ensure that your website has all the links to your social media pages.
18. User-Generated Content
The next is user generated content also call UGC , it’s a content that generated by your customers. Till now there is no problem in the user generated content but if you forgot UGC tag it will become your product page content then it will create a problem. So check in the customer reviews that all reviews should Mark with ugc tag.
19. Site Speed
As I mentioned earlier, page speed is a ranking signal. Therefore, check the speed of your website on both desktop and phone using the PageSpeed Insights tool. If your site scores above 82, it’s a positive indicator, and if it passes the Core Web Vitals, congratulations, that’s a significant achievement. However, if your site takes more than 2.5 seconds to load, please work on improving it.
Ecommerce – Off-Page SEO Audit
The E-commerce Off-Page SEO Audit includes only three things: Domain Authority, Page Authority, and toxic links in the backlink types (dofollow and nofollow). These three sections are collectively referred to as off-page SEO. Other websites may have many more off-page SEO activities such as influencer marketing , which is beneficial, but they are not part of the SEO audit; rather, they are part of off-page SEO activities.
20. Domain Authority & Page Authority
Conduct an audit of your website’s Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA); these are essential metrics for ranking. If the Domain Authority is below 10, it needs improvement, and the same applies to Page Authority.
You can use Ahrefs’ free Website Authority checker tool.
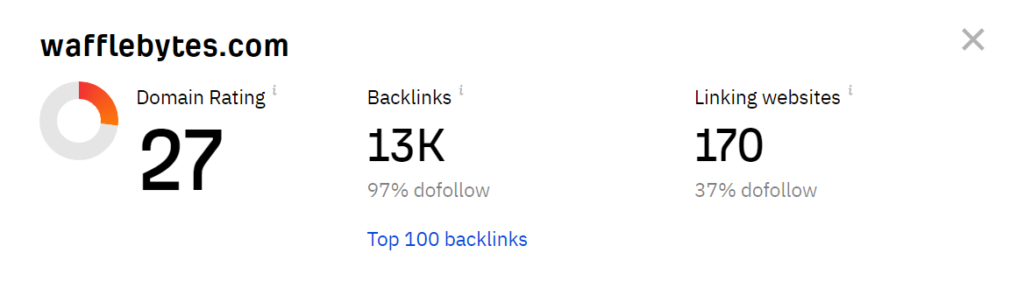
21. Backlinks – Dofollow & Nofollow
Check how many do-follow backlinks the website currently has in referring domains as well. The number and quality of do-follow backlinks significantly impact SEO, website authority, and rankings. Here’s why they matter:
- Search Engine Ranking: Backlinks act as votes of confidence for your site, influencing higher rankings on search engines like Google, especially with high-quality links from reputable sources.
- Website Authority: Backlinks from authoritative sites enhance your website’s trustworthiness and overall authority in the eyes of search engines.
- Referral Traffic: Do-follow backlinks drive direct traffic to your site when users click on links from other websites, increasing visibility and potential conversions.
- Indexing and Crawling: Backlinks help search engine crawlers discover and index your web pages, making your content accessible in search results.
- Diversity and Relevance: A diverse backlink profile from relevant domains boosts your site’s visibility and relevance across various topics.
22. Toxic Backlinks
This is the last thing to do in e-commerce SEO audit. Look for toxic and spammy backlinks coming from irrelevant sites, and if you find any, try to remove them.
Final Words
These 22 things will help you fix SEO issues on your e-commerce website. If you are unable to do this yourself, you can contact us. We have experienced SEO executives who can resolve the issues quickly and deliver excellent results.
Lastly, be patient; SEO is a continuous activity that takes time to show results. It may take 3-6 months to see the first impact, so exercise patience and adhere to search engine guidelines.
Feel free to comment if we missed something, and we will provide our point of view on that aspect.
Thank you!

